In the field of IT infrastructure, Cisco is the top most vendor. Candidates seeking to make their career in IT networking start with Cisco enterprise CCNA. In this article, you'll get to know about ccna course syllabus.
Based on ccna 200-301 syllabus , the ccna examination awards you the certification which has a good reputation in the industry for the last more than couple of decades.
The broad topics from latest Cisco CCNA syllabus:
It assesses your understanding and abilities in areas such as
1. Network fundamentals
2. Network Access
3. IP Connectivity
4. IP Services
5. Security Fundamentals
6. Automation and programmability
There are couple of ways by which you can learn and understand all the concepts, remember you'll not be able to learn concepts until you do a lot of hands-on labs.
Self Study - In which you read and refer a lot of books with labs though self paced ccna training videos can be a great help.
Live Training - You can attend interactive session with instructor in ccna course online, this can be the fastest way the learn. However self study with lab is still required.
The following are the general guidelines for the exam content, however Cisco keep introducing additional related topics in exam to check the active preparation of the candidates.
They may also change the exam format without prior notice in order to accurately represent the exam's contents and ensure clarity.
Check Cisco website for the most updated announcement on CCNA syllabus or you can directly contact to our learning advisor for any help related to CCNA.
Detailed CCNA Course Syllabus
1.0 Network Fundamentals
1.1 Explain the role and function of network hardware devices
1.1.a Routers
1.1.b Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches
1.1.c Next-generation firewalls and IPS
1.1.d Access points
1.1.e Controllers (Cisco DNA Center and WLC)
1.1.f Endpoints
1.1.g Servers
1.1.h PoE
1.2 Describe different types network topologies
1.2.a Two-tier
1.2.b Three-tier
1.2.c Spine-leaf
1.2.d WAN
1.2.e Small office/home office (SOHO)
1.2.f On-premises and cloud
1.3 Compare computer network cable types
1.3.a Single-mode fiber, multimode fiber, copper
1.3.b Connections (Ethernet shared media and point-to-point)
1.4 Identify interface and cable issues (collisions, errors, mismatch duplex, and/or speed)
1.6 Configure and verify IPv4 addressing and subnetting
1.7 Describe the need for private IPv4 addressing
1.8 Configure and verify IPv6 addressing and prefix
1.9 Describe IPv6 address types
1.9.a Unicast (global, unique local, and link local)
1.9.b Anycast
1.9.c Multicast
1.9.d Modified EUI 64
1.10 Verify IP parameters for Client OS (Windows, Mac OS, Linux)
1.11 Describe wireless principles
1.11.a Nonoverlapping Wi-Fi channels
1.11.b SSID
1.11.c RF
1.11.d Encryption
1.12 Explain virtualization fundamentals (server virtualization, containers, and VRFs)
1.13 Describe switching concepts.
1.13.b Frame switching
2.0 Network Access
2.1 Configure and verify VLANs (normal range) spanning multiple switches
2.1.a Access ports (data and voice)
2.1.b Default VLAN
2.2 Configure and verify interswitch connectivity
2.3 Configure and verify Layer 2 discovery protocols (Cisco Discovery Protocol and LLDP)
2.4 Configure and verify (Layer 2/Layer 3) EtherChannel (LACP)
2.5 Interpret basic operations of Rapid PVST+ Spanning Tree Protocol
2.5.a Root port, root bridge (primary/secondary), and other port names
2.5.b Port states (forwarding/blocking)
2.6 Describe Cisco Wireless Architectures and AP modes (Basics of wireless communication or principles)
2.7 Describe physical infrastructure connections of WLAN components (AP, WLC, access/trunk ports, and LAG)
2.8 Describe AP and WLC management access connections (Telnet, SSH, HTTP, HTTPS, console, and TACACS+/RADIUS)
2.9 Interpret the wireless LAN GUI configuration for client connectivity, such as WLAN creation, security settings, QoS profiles, and advanced settings
3.0 IP Connectivity
3.1 Interpret the components of routing table
3.1.a Routing protocol code
3.1.b Prefix
3.1.c Network mask
3.1.d Next hop
3.1.e Administrative distance
3.1.f Metric
3.1.g Gateway of last resort
3.2 Determine how a router makes a forwarding decision by default
3.2.a Longest prefix match
3.2.b Administrative distance
3.2.c Routing protocol metric
3.3 Configure and verify IPv4 and IPv6 static routing
3.3.b Network route
3.3.c Host route
3.3.d Floating static
3.4 Configure and verify single area OSPFv2
3.4.a Neighbor adjacencies
3.4.b Point-to-point
3.4.c Broadcast (DR/BDR selection)
3.4.d Router ID
3.5 Describe the purpose, functions, and concepts of first hop redundancy protocols
4.0 IP Services
4.1 Configure and verify inside source NAT using static and pools
4.2 Configure and verify NTP operating in a client and server mode
4.3 Explain the role of DHCP and DNS within the network
4.4 Explain the function of SNMP in network operations
4.5 Describe the use of syslog features including facilities and levels
4.6 Configure and verify DHCP client and relay
4.7 Explain the forwarding per-hop behavior (PHB) for QoS, such as classification, marking, queuing, congestion, policing, and shaping
4.8 Configure network devices for remote access using SSH
4.9 Describe the capabilities and functions of TFTP/FTP in the network
5.0 Security Fundamentals
5.1 Define key security concepts (threats, vulnerabilities, exploits, and mitigation techniques)
5.2 Describe security program elements (user awareness, training, and physical access control)
5.3 Configure and verify device access control using local passwords
5.4 Describe security password policies elements, such as management, complexity, and password alternatives (multifactor authentication, certificates, and biometrics)
5.5 Describe IPsec remote access and site-to-site VPNs
5.6 Configure and verify access control lists
5.7 Configure and verify Layer 2 security features (DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP inspection, and port security)
5.8 Compare authentication, authorization, and accounting concepts
5.9 Describe wireless security protocols (WPA, WPA2, and WPA3)
5.10 Configure and verify WLAN within the GUI using WPA2 PSK
6.0 Automation and Programmability
6.1 Explain how automation impacts network management
6.2 Compare traditional networks with controller-based networking
6.3 Describe controller-based, software defined architecture (overlay, underlay, and fabric)
6.3.a Separation of control plane and data plane
6.3.b Northbound and Southbound APIs
6.4 Compare traditional campus device management with Cisco DNA Center enabled device management
6.5 Describe characteristics of REST-based APIs (CRUD, HTTP verbs, and data encoding)
6.6 Recognize the capabilities of configuration management mechanisms Puppet, Chef, and Ansible
6.7 Recognize components of JSON-encoded data
Related Articles:
Difference Between Router and Switch
Comments (0)
Categories
Popular posts

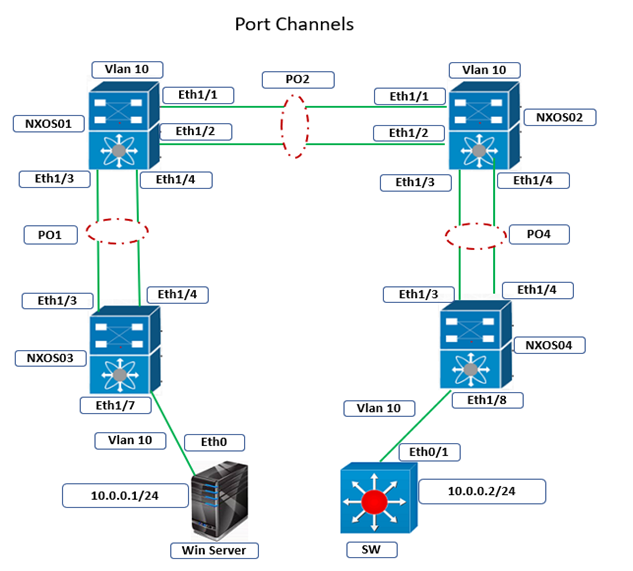
Cisco Nexus Port Channel: Configuring ...
26 Apr 2024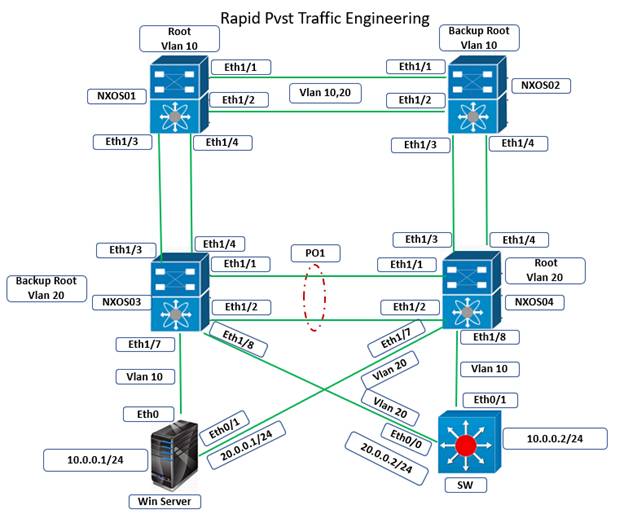
Configure Rapid PVST on Cisco Nexus
26 Apr 2024
Palo Alto Exam Cost: PCNSA, PCNSE & More
27 Apr 2024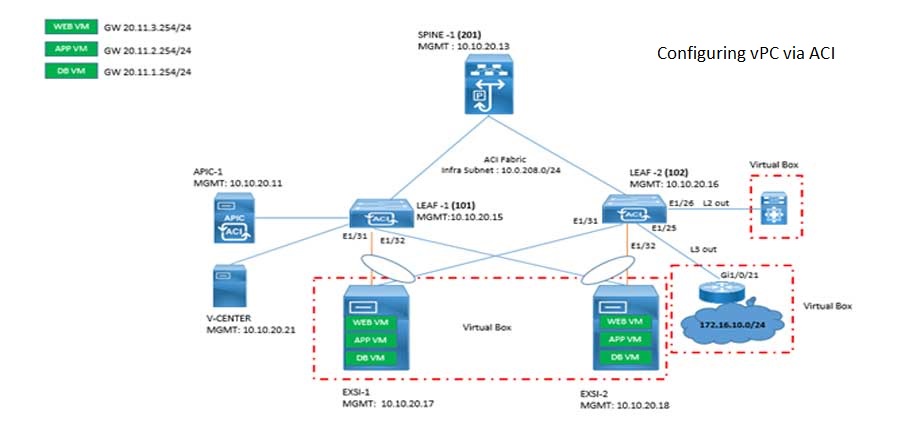
Cisco ACI VPC Configuration Task Steps
28 Apr 2024Recent posts

What is Cisco ACI: Overview and Benefits
28 Apr 2024
Cisco ACI vs Nexus: Comparison
28 Apr 2024
Cisco ACI VPC Configuration Task Steps
28 Apr 2024
CCNP Certification Cost and Exam Fees
27 Apr 2024